3、写入数据
1、基于模板导出列表数据
首先准备一个excel模板,这个模板把复杂的样式和固定的内容先准备好并且放入到项目中,然后读取到模板后向里面放入数据。
1、准备工作
准备模板内容
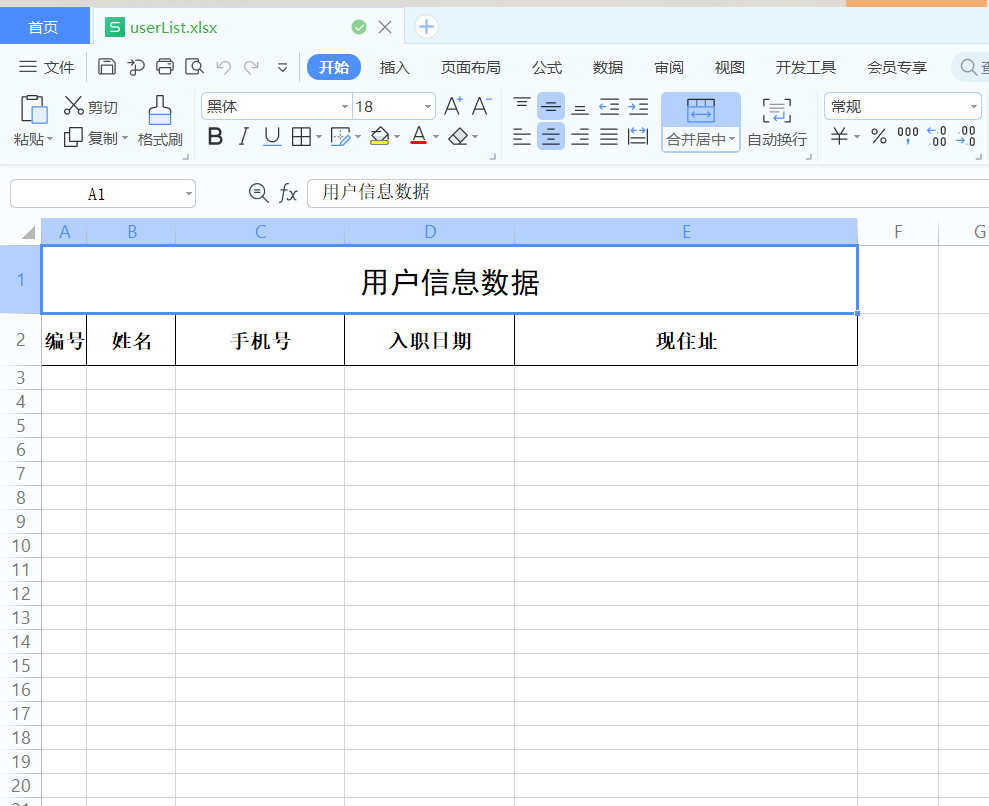
第二个sheet页
把这个模板改一个英文名称比如:userList.xlsx,放入到项目中
2、步骤
- 获取模板路径
- 获取我们设置的样式
- 处理数据
- 导出
3、实现
/**
* 通过模板下载
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws Exception
*/
public void exportUserByTemplate(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception{
//获取根目录路径 SpringBoot项目获取根目录的方式
String classpath = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:").getPath();
File file = new File(classpath);
//模板路径
File templatePath = new File(file.getAbsolutePath(), "/excel_template/userList.xlsx");
//读取模板文件产生workbook对象,这个workbook是一个有内容的工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(templatePath);
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取我们设置好的样式
CellStyle contentStyle = workbook.getSheetAt(1).getRow(0).getCell(0).getCellStyle();
// 处理内容
List<User> userList = this.findAll();
int rowIndex = 2;
Row row = null;
Cell cell;
for (User user : userList) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
row.setHeightInPoints(15);
cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getId());
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getUserName());
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getPhone());
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
cell = row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getAddress());
rowIndex++;
}
//删除之前多余的sheet
workbook.removeSheetAt(1);
// 导出的文件名称
String filename="员工数据.xlsx";
// 设置文件的打开方式和mime类型
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
response.setHeader( "Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String(filename.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
workbook.write(outputStream);
}2、基于模板导出详细数据
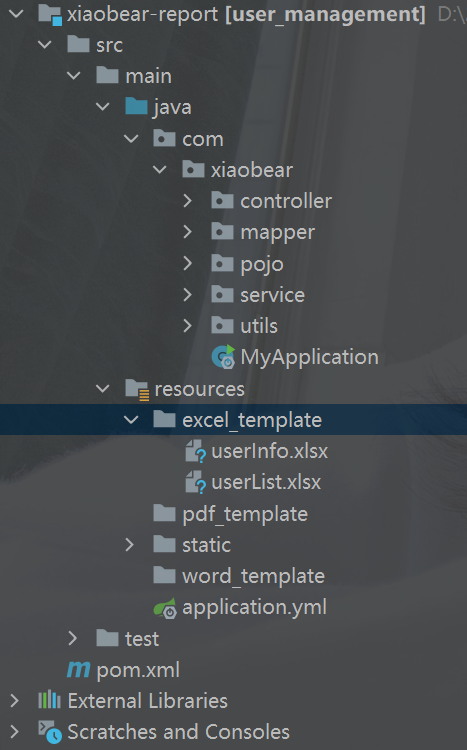
要做成这样的

1、准备工作
制作一个excel导出模板,如下
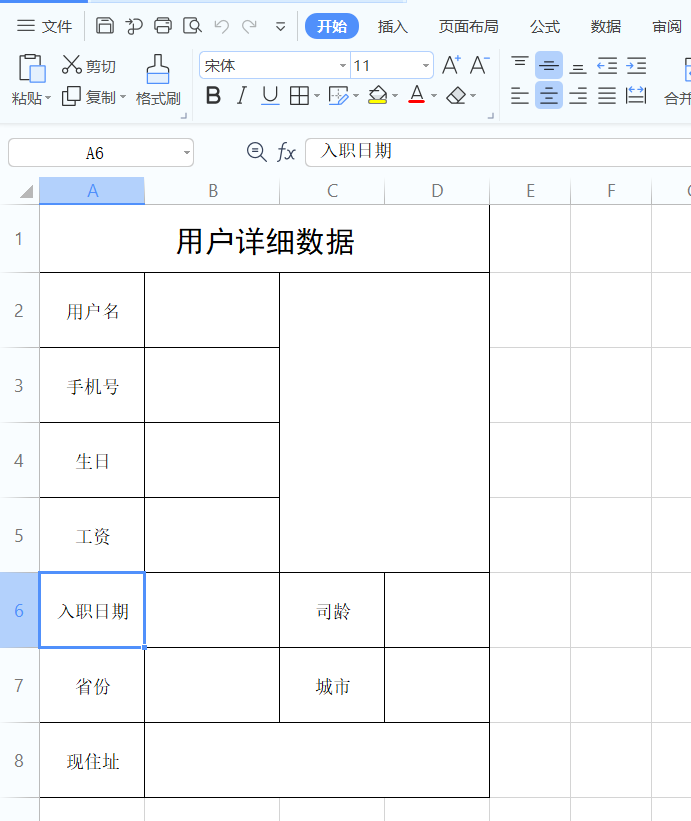
制作好的模板放入到项目中
2、代码实现
/**
* 通过模板下载
* @param id
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws IOException
* @throws InvalidFormatException
*/
public void downLoadUserInfoByTemplate(Long id, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
//获取根目录
File root = new File(ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:").getPath());
//获取模板路径
File file = new File(root.getAbsolutePath(), "/excel_template/userInfo.xlsx");
//获取工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//获取sheet页
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取数据源
User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
//设置用户名
sheet.getRow(1).getCell(1).setCellValue(user.getUserName());
//设置手机号
sheet.getRow(2).getCell(1).setCellValue(user.getPhone());
// 生日 第4行第2列 日期转成字符串
sheet.getRow(3).getCell(1).setCellValue(sd.format(user.getBirthday()));
// 工资 第5行第2列
sheet.getRow(4).getCell(1).setCellValue(user.getSalary());
// 工资 第6行第2列
sheet.getRow(5).getCell(1).setCellValue(sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
//省份 第7行第2列
sheet.getRow(6).getCell(1).setCellValue(user.getProvince());
//现住址 第8行第2列
sheet.getRow(7).getCell(1).setCellValue(user.getAddress());
//司龄 第6行第4列暂时先不考虑
//城市 第7行第4列
sheet.getRow(6).getCell(3).setCellValue(user.getCity());
String fileName = "用户详细数据导出测试.xlsx";
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;fileName=" + new String(fileName.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
workbook.write(response.getOutputStream());
}3、导出数据带图片以及公式
1、图片
POI主要提供了两个类来处理照片,这两个类是Patriarch和ClientAnchor前者负责在表中创建图片,后者负责设置图片的大小位置。
//用户头像数据 创建一个字节输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//获取图片信息 BufferedImage是一个带缓冲区图像类,主要作用是将一幅图片加载到内存中
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(new File(root, user.getPhoto()));
//把读取图片放入输出流中
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",byteArrayOutputStream);
// 创建一个绘图控制类,负责画图
Drawing<?> patriarch = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
// 指定把图片放到哪个位置
XSSFClientAnchor clientAnchor = new XSSFClientAnchor(0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 4, 5);
// 开始把图片写入到sheet指定的位置
patriarch.createPicture(clientAnchor, workbook.addPicture(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(), org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook.PICTURE_TYPE_JPEG));关于XSSFClientAnchor的8个参数说明:
dx1 - the x coordinate within the first cell.//定义了图片在第一个cell内的偏移x坐标,既左上角所在cell的偏移x坐标,一般可设0
dy1 - the y coordinate within the first cell.//定义了图片在第一个cell的偏移y坐标,既左上角所在cell的偏移y坐标,一般可设0
dx2 - the x coordinate within the second cell.//定义了图片在第二个cell的偏移x坐标,既右下角所在cell的偏移x坐标,一般可设0
dy2 - the y coordinate within the second cell.//定义了图片在第二个cell的偏移y坐标,既右下角所在cell的偏移y坐标,一般可设0
col1 - the column (0 based) of the first cell.//第一个cell所在列,既图片左上角所在列
row1 - the row (0 based) of the first cell.//图片左上角所在行
col2 - the column (0 based) of the second cell.//图片右下角所在列
row2 - the row (0 based) of the second cell.//图片右下角所在行2、公式
关于POI支持公式详见官网: https://poi.apache.org/components/spreadsheet/eval-devguide.html
ps:其实在正常开发时应该在模板中直接设置好公式,这样打开直接导出的excel文档时公式会直接运行出我们想要的结果
sheet.getRow(5).getCell(3).setCellFormula("DATEDIF(B6,TODAY(),\"y\")");4、基于模板引擎(按照字段写入)
1、说明
看我们刚才导出时写的代码,必须要提前知道要导出数据在哪一行哪一个单元格,但是如果模板一旦发生调整,那么我们的java代码必须要修改,我们可以自定义个导出的引擎,有了这个引擎即使模板修改了我们的java代码也不用修改
2、思路
在制作模板时,在需要插入数据的位置我们坐上标记,在导出时,对象的属性要和标记做对应,如果对应匹配一样,就把值赋值到相应的位置。
标记:通常是我们导出的字段,这样检查也好一点
3、实现
制作模板
添加到项目中
4、代码实现
模板引擎的工具类:
public class ExcelEngineUtils {
private static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
/**
*
* @param object
* @param workbook
* @param photoPath
* @return
*/
public static Workbook writeToExcel(Object object, Workbook workbook, String photoPath) throws IOException {
//先把bean转成map
Map<String, Object> map = EntityUtils.entityToMap(object);
//循环遍历每一对数据,把日期型的转成字符串
for (String s : map.keySet()) {
Object o = map.get(s);
if (o instanceof Date){
map.put(s,sdf.format(o));
}
}
//获取第一个sheet
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Cell cell;
Row row;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//不知道数据有多少行的情况下,当获取row为null,退出循环
row = sheet.getRow(i);
if (null == row){
break;
}else {
//不为空,获取单元格的数据
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
cell = row.getCell(j);
//写入单元格
if(null != cell){
writeCell(cell,map);
}
}
}
}
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(photoPath)){
//获取根目录
File root = new File(ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:").getAbsolutePath());
//创建一个字节输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream arrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//获取图片信息 BufferedImage是一个带缓冲区图像类,主要作用是将一幅图片加载到内存中
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(new File(root, photoPath));
// 把读取图片放入输出流中
ImageIO.write(image,"jpg",arrayOutputStream);
Drawing<?> drawingPatriarch = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch();
//获取第二个sheet页的坐标
Sheet sheet1 = workbook.getSheetAt(1);
Row row0 = sheet1.getRow(0);
int col1 = ((Double) row0.getCell(0).getNumericCellValue()).intValue();
int row1 = ((Double) row0.getCell(1).getNumericCellValue()).intValue();
int col2 = ((Double) row0.getCell(2).getNumericCellValue()).intValue();
int row2 = ((Double) row0.getCell(3).getNumericCellValue()).intValue();
XSSFClientAnchor clientAnchor = new XSSFClientAnchor(0, 0, 0, 0, col1, row1, col2, row2);
drawingPatriarch.createPicture(clientAnchor,workbook.addPicture(arrayOutputStream.toByteArray(), Workbook.PICTURE_TYPE_JPEG));
workbook.removeSheetAt(1);
}
return workbook;
}
/**
* 写入单元格信息
* @param cell
* @param map
*/
public static void writeCell(Cell cell, Map<String, Object> map){
//获取单元格类型
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
switch (cellType){
case FORMULA:{
break;
} default:{
String cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
//就是判断一下获取到单元格中的值是否和map中的key保持一致
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(cellValue)){
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
if(key.equals(cellValue)){
cell.setCellValue(map.get(key).toString());
}
}
}
}
}
}
}调用
/**
* 通过模板引擎导出
* @param id
* @param request
* @param response
*/
public void downLoadUserInfoByTemplateEngine(Long id, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
File root = new File(ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:").getPath());
//获取图片路径
File file = new File(root.getAbsolutePath(), "/excel_template/userInfo2.xlsx");
//获取工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//查询用户信息
User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook wb = ExcelEngineUtils.writeToExcel(user, workbook, user.getPhoto());
String fileName = "用户模板引擎导出测试.xlsx";
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=" + new String(fileName.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
workbook.write(response.getOutputStream());
}5、百万数据导出
1、概述
我们都知道Excel可以分为早期的Excel2003版本(使用POI的HSSF对象操作)和Excel2007版本(使用POI的XSSF操作),两者对百万数据的支持如下:
- Excel 2003:在POI中使用HSSF对象时,excel 2003最多只允许存储65536条数据,一般用来处理较少的数据量。这时对于百万级别数据,Excel肯定容纳不了。
- Excel 2007:当POI升级到XSSF对象时,它可以直接支持excel2007以上版本,因为它采用ooxml格式。这时excel可以支持1048576条数据,单个sheet表就支持近百万条数据。但实际运行时还可能存在问题,原因是执行POI报表所产生的行对象,单元格对象,字体对象,他们都不会销毁,这就导致OOM的风险。
2、思路
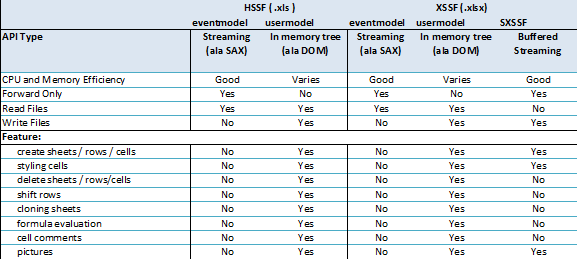
对于百万数据量的Excel导入导出,只讨论基于Excel2007的解决方法。在ApachePoi 官方提供了对操作大数据量的导入导出的工具和解决办法,操作Excel2007使用XSSF对象,可以分为三种模式:
- java代码解析xml
- dom4j:一次性加载xml文件再解析
- SAX:逐行加载,逐行解析
**用户模式:**用户模式有许多封装好的方法操作简单,但创建太多的对象,非常耗内存(之前使用的方法)
**事件模式:**基于SAX方式解析XML,SAX全称Simple API for XML,它是一个接口,也是一个软件包。它是一种XML解析的替代方法,不同于DOM解析XML文档时把所有内容一次性加载到内存中的方式,它逐行扫描文档,一边扫描,一边解析。
SXSSF对象:是用来生成海量excel数据文件,主要原理是借助临时存储空间生成excel
3、导出
1、模拟数据
创建表
CREATE TABLE `tb_user2` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户ID', `user_name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `phone` varchar(15) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号', `province` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '省份', `city` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '城市', `salary` int(10) DEFAULT NULL, `hire_date` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '入职日期', `dept_id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '部门编号', `birthday` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '出生日期', `photo` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '照片路径', `address` varchar(300) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '现在住址' ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;创建存储过程
DELIMITER $$ -- 重新定义“;”分号 DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS test_insert $$ -- 如果有test_insert这个存储过程就删除 CREATE PROCEDURE test_insert() -- 创建存储过程 BEGIN DECLARE n int DEFAULT 1; -- 定义变量n=1 SET AUTOCOMMIT=0; -- 取消自动提交 while n <= 5000000 do INSERT INTO `tb_user2` VALUES ( n, CONCAT('测试', n), '13800000001', '北京市', '北京市', '11000', '2001-03-01 21:18:29', '1', '1981-03-02 00:00:00', '\\static\\user_photos\\1.jpg', '北京市西城区宣武大街1号院'); SET n=n+1; END while; COMMIT; END $$开始执行
CALL test_insert();插入500W数据大概需要200至300秒左右
/**
* 百万数据导出
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws IOException
*/
public void downLoadMillionData(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//创建工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook sxssfWorkbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
int page = 1;
int pageSize = 200000;
Sheet sheet = null;
int rowIndex = 1;
int num = 0; //总数据量
Cell cell;
Row row;
while(true){
//用户分页 1000000为一页
List<User> userList = this.findPage(page, pageSize);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userList)){
break;
}
if(num % 1000000 == 0){
rowIndex = 1;
sheet = sxssfWorkbook.createSheet("第" + num/1000000 + "个工作表");
//设置列宽
sheet.setColumnWidth(0,8*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(1,12*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(3,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(4,30*256);
// 处理标题
String[] titles = new String[]{"编号","姓名","手机号","入职日期","现住址"};
// 创建标题行
Row titleRow = sheet.createRow(0);
for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {
cell = titleRow.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(titles[i]);
}
}
//处理数据
for (User user : userList) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(user.getId());
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue(user.getUserName());
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(user.getPhone());
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue(sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellValue(user.getAddress());
num++;
rowIndex++;
}
page++;
}
// 导出的文件名称
String filename="百万数据.xlsx";
// 设置文件的打开方式和mime类型
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
response.setHeader( "Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String(filename.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
sxssfWorkbook.write(outputStream);
}6、百万数据导入
1、思路分析
**用户模式:**加载并读取Excel时,是通过一次性的将所有数据加载到内存中再去解析每个单元格内容。当Excel数据量较大时,由于不同的运行环境可能会造成内存不足甚至OOM异常。
**事件模式:**它逐行扫描文档,一边扫描一边解析。由于应用程序只是在读取数据时检查数据,因此不需要将数据存储在内存中,这对于大型文档的解析是个巨大优势。
2、实现
1、步骤分析
设置POI的事件模式
根据Excel获取文件流
根据文件流创建OPCPackage 用来组合读取到的xml 组合出来的数据占用的空间更小
创建XSSFReader对象Sax解析
自定义Sheet处理器
创建Sax的XmlReader对象
设置Sheet的事件处理器
逐行读取
2、自定义处理器
public class SheetHandle extends XSSFSheetXMLHandler implements XSSFSheetXMLHandler.SheetContentsHandler {
private User user;
public SheetHandle(Styles styles, Comments comments, SharedStrings strings, SheetContentsHandler sheetContentsHandler, DataFormatter dataFormatter, boolean formulasNotResults) {
super(styles, comments, strings, sheetContentsHandler, dataFormatter, formulasNotResults);
}
/**
* 每一行的开始
* @param i 代表的是每一个sheet的行索引
*/
@Override
public void startRow(int i) {
if (0 == i){
user = null;
}else {
user = new User();
}
}
/**
* 每一行的结束
* @param i
*/
@Override
public void endRow(int i) {
if(0 != i){
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/**
* 处理每一行的单元格
* @param s 单元格名称 A1 B2
* @param s1 单元格的值
* @param xssfComment
*/
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void cell(String s, String s1, XSSFComment xssfComment) {
if (user != null) {
//获取单元格首个字符
String substring = s.substring(0, 1);
switch (substring){
case "A":{
user.setId(Long.parseLong(s1));
break;
} case "B":{
user.setUserName(s1);
break;
} case "C":{
user.setPhone(s1);
break;
} case "D":{
user.setHireDate(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse(s1));
break;
}case "E":{
user.setAddress(s1);
break;
}
}
}
}
}3、自定义解析
public class ExcelParser {
public static void parse(String path) throws Exception {
//1.根据Excel获取OPCPackage对象
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(path, PackageAccess.READ);
try {
//2.创建XSSFReader对象
XSSFReader reader = new XSSFReader(pkg);
//3.获取SharedStringsTable对象
SharedStringsTable sst = reader.getSharedStringsTable();
//4.获取StylesTable对象
StylesTable styles = reader.getStylesTable();
XMLReader parser = XMLReaderFactory.createXMLReader();
// 处理公共属性:Sheet名,Sheet合并单元格
parser.setContentHandler(new XSSFSheetXMLHandler(styles,sst, new SheetHandle(styles,null,sst,null,null,false), false));
XSSFReader.SheetIterator sheets = (XSSFReader.SheetIterator) reader.getSheetsData();
while (sheets.hasNext()) {
InputStream sheetstream = sheets.next();
InputSource sheetSource = new InputSource(sheetstream);
try {
parser.parse(sheetSource);
} finally {
sheetstream.close();
}
}
} finally {
pkg.close();
}
}
}