2、Excel
1、Excel简介
在企业级应用开发中,Excel报表是一种最常见的报表需求。Excel报表开发一般分为两种形式:
1、为了方便操作,基于Excel的报表批量上传数据,也就是把Excel中的数据导入到系统中。
2、通过java代码生成Excel报表。也就是把系统中的数据导出到Excel中,方便查阅。
1、Excel版本
目前世面上的Excel分为两个大的版本Excel2003和Excel2007及以上两个版本;
| Excel2003 | Excel2007 | |
|---|---|---|
| 后缀 | xls | xlsx |
| 结构 | 二进制格式,核心是复合文档类型结构 | XML类型结构 |
| 单sheet数量 | 行:65525,列:256 | 行:1048576,列:16384 |
| 特点 | 存储容量有限 | 基于xml压缩,占用空间小,操作效率高 |
2、常见的Excel操作工具
Java中常见的用来操作Excel的方式一般有2种:JXL和POI。
1、JXL
JXL只能对Excel进行操作,属于比较老的框架,它只支持到Excel 95-2000的版本。现在已经停止更新和维护.
2、POI
POI是apache的项目,可对微软的Word,Excel,PPT进行操作,包括office2003和2007,Excle2003和2007。poi现在一直有更新。所以现在主流使用POI。
Apache POI是Apache软件基金会的开源项目,由Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的 Java API,ApachePOI提供API给Java语言操作Microsoft Office的功能。
API对象介绍
| Excle2003 | Excle2007 | |
|---|---|---|
| 工作簿(WorkBook) | HSSFWordBook | XSSFWorkBook |
| 工作表(Sheet) | HSSFSheet | XSSFSheet |
| 行(Row) | HSSFRow | XSSFRow |
| 单元格(Cell) | HSSFCell | XSSCell |
2、JXL导出excel
1、JXL导出基本知识点
通过WritableWorkbook,WritableSheet,Label这三个对象我们就可以实现Excel文件的导出工作。
1、 创建可写入的Excel工作薄
WritableWorkbook workbook= Workbook.createWorkbook(输出流);2、创建工作表
WritableSheet sheet= workbook.createSheet(工作表的名称, 工作表的索引值);3、创建单元格,添加文本类单元格
Label labelC = new Label(列索引值, 行索引值, "单元格中的内容");
sheet.addCell(labelC);4、写入到文件
workbook.write();// 写入数据5、释放资源:
workbook.close();// 关闭文件2、代码实现
/**
* 通过JSL进行下载
* @param response
*/
public void downLoadByJxl(HttpServletResponse response){
try{
//输出流
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
//创建一个工作簿
WritableWorkbook wb = Workbook.createWorkbook(outputStream);
//创建一个sheet页 s:sheet名 i:sheet号
WritableSheet wbSheet = wb.createSheet("xiaobear第一个报表文件", 0);
//设置列宽 col:列 wid:宽d
wbSheet.setColumnView(0,5);
wbSheet.setColumnView(1,8);
wbSheet.setColumnView(2,8);
wbSheet.setColumnView(3,8);
wbSheet.setColumnView(4,10);
wbSheet.setColumnView(5,30);
//创建单元格
// Label labelC = new Label(列索引值, 行索引值, "单元格中的内容");
//sheet.addCell(labelC);
Label label = null;
String[] titles = new String[]{"编号","名称","电话","生日","入职日期","住址"};
//处理标题
for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {
label = new Label(i, 0, titles[i]);
wbSheet.addCell(label);
}
//查询数据进行处理
List<User> users = findAll();
//行初始化值
int rowIndex = 1;
for (User user : users) {
//编号
label = new Label(0, rowIndex, user.getId().toString());
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//名称
label = new Label(1, rowIndex, user.getUserName());
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//电话
label = new Label(2, rowIndex, user.getPhone());
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//生日
label = new Label(3, rowIndex, sd.format(user.getBirthday()));
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//入职日期
label = new Label(4, rowIndex, sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//地址
label = new Label(5, rowIndex, user.getAddress());
wbSheet.addCell(label);
//行+1
rowIndex++;
}
//导出的文件名称
String fileName = "JXL导出示例.xls";
// 设置文件的打开方式和mime类型
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename=" + new String(fileName.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
//导出
wb.write();
//关闭资源
wb.close();
outputStream.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3、POI操作Excel
<!--poi所需要的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml-schemas</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>1、版本之间的区别
在POI包中有如下几个主要对象和excel的几个对象对应:
| 对应excel名称 | 低版本中的类名 | 高版本中的类名 |
|---|---|---|
| 工作簿 | HSSFWorkbook | XSSFWorkbook |
| 工作表 | HSSFSheet | XSSFSheet |
| 行 | HSSFRow | XSSFRow |
| 单元格 | HSSFCell | XSSFCell |
| 单元格样式 | HSSFCellStyle | XSSFCellStyle |
1、2003操作excel
/**
* 通过低版本创建excel
*/
public static void CreateExcelBy2003() throws IOException {
//创建一个工作簿
HSSFWorkbook hssfWorkbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//创建一个sheet页
HSSFSheet sheet = hssfWorkbook.createSheet("低版本");
//创建行
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建列
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(0);
//创建单元格
cell.setCellValue("xiaobear so nice");
hssfWorkbook.write(new FileOutputStream("D://test.xls"));
}2、2007操作excel
/**
* 通过高版本创建excel
*/
public static void CreateExcelBy2007() throws IOException {
//创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//创建一个sheet页
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("低版本");
//创建行
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
//创建列
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
//创建单元格
cell.setCellValue("xiaobear so nice");
workbook.write(new FileOutputStream("D://test.xls"));
}2、数据导入
数据的导入就是读取excel中的内容,转成对象插入到数据库中
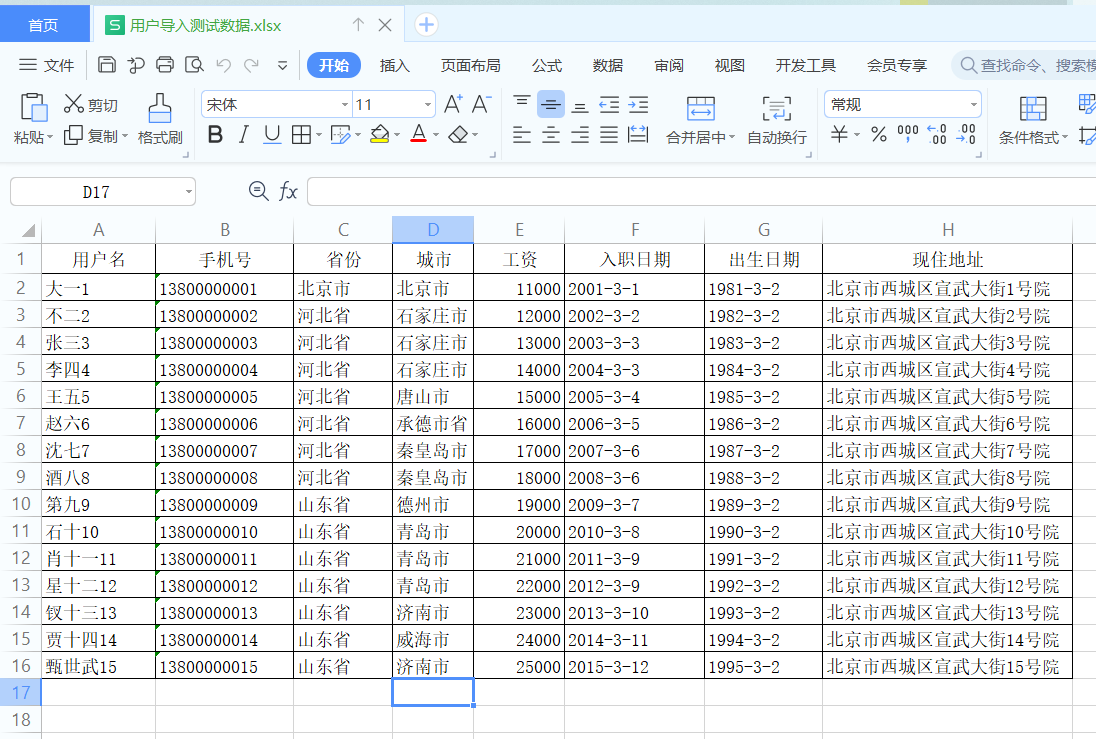
导入上图的数据
1、思路
一般来说,即将导入的文件,每个列代表什么意思基本上都是固定的,比如第1列就是用户姓名,最后一列就是用户的现住址,并且在做excel时对每个列的类型都是有要求的,这样就可以给我们开发带来很大的简便。
最终的目标就是读取每一行数据,把数据转成用户的对象,保存到表中
步骤:
- 根据上传的文件创建Workbook
- 获取到第一个sheet工作表
- 从第二行开始读取数据
- 读取每一个单元格,把内容放入到用户对象的相关的属性中
2、代码实现
/**
* 用户导入数据
* @param file
* @throws IOException
* @throws ParseException
*/
public void importUserByExcel(MultipartFile file) throws IOException, ParseException {
//通过文件流返回一个工作薄
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(file.getInputStream());
//获取第一个sheet页
XSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
//获取最后一行
int lastRowNum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
//遍历获取数据 开始循环每行,获取每行的单元格中的值,放入到user属性中
User user;
for (int i = 1; i <= lastRowNum ; i++) {
user = new User();
String userName = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(0).getStringCellValue();
user.setUserName(userName);
//手机号
String phone = null;
try {
phone = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(1).getStringCellValue();
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
phone = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(1).getNumericCellValue()+"";
}
user.setPhone(phone);
//省份
String province = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(2).getStringCellValue();
//城市
String city = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(3).getStringCellValue();
user.setCity(city);
// 因为在填写excel中的数据时就可以约定这个列只能填写数值,所以可以直接用getNumericCellValue方法
//工资
Integer salary = ((Double)sheet.getRow(i).getCell(4).getNumericCellValue()).intValue();
user.setSalary(salary);
//入职日期
String hireDateStr = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(5).getStringCellValue();
Date hireDate = sd.parse(hireDateStr);
user.setHireDate(hireDate);
//出生日期
String birthdayStr = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(6).getStringCellValue();
Date birthday = sd.parse(birthdayStr);
user.setBirthday(birthday);
//现住地址
String address = sheet.getRow(i).getCell(7).getStringCellValue();
user.setProvince(province);
user.setAddress(address);
userMapper.insert(user);
}
}3、数据导出
用户导出跟JXL导出差不多
/**
* 用户导出
* @param response
* @throws IOException
*/
public void exportUser(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 创建一个空的工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 在工作薄中创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("测试");
// 设置列宽
sheet.setColumnWidth(0,5*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(1,12*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(3,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(4,30*256);
// 处理标题
String[] titles = new String[]{"编号","姓名","手机号","入职日期","现住址"};
// 创建标题行
Row titleRow = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cell = null;
for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {
cell = titleRow.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(titles[i]);
}
// 处理内容
List<User> userList = this.findAll();
int rowIndex = 1;
Row row = null;
for (User user : userList) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getId());
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getUserName());
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getPhone());
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
cell = row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getAddress());
rowIndex++;
}
// 导出的文件名称
String filename="员工数据.xlsx";
// 设置文件的打开方式和mime类型
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
response.setHeader( "Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String(filename.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
workbook.write(outputStream);
}4、设置样式
注:所有样式需在单元格被创建之后才能设置,否则就会报空指针
1、设置边框
CellStyle contentStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
contentStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);2、对齐方式
//设置居中对齐
contentStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
contentStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);3、合并单元格
//合并单元格 起始行, 结束行, 起始列, 结束列
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0,0,0,4));4、设置行高
//设置行高
row1.setHeightInPoints((short) 52);5、设置字体样式
//设置字体
CellStyle titleStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBold(true);
font.setFontName("黑体");
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 16);
titleStyle.setFont(font);5、完整导出代码
/**
* 用户导出
* @param response
* @throws IOException
*/
public void exportUser(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// 创建一个空的工作薄
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 在工作薄中创建一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("测试");
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
//设置行高
row1.setHeightInPoints((short) 52);
//合并单元格
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0,0,0,4));
// 设置列宽
sheet.setColumnWidth(0,5*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(1,12*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(2,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(3,15*256);
sheet.setColumnWidth(4,30*256);
/**
* 设置框线
*/
CellStyle contentStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
contentStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
contentStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
//设置居中对齐
contentStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
contentStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
//设置字体
CellStyle titleStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setBold(true);
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 16);
titleStyle.setFont(font);
titleStyle.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
titleStyle.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
titleStyle.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
titleStyle.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
//设置居中对齐
titleStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
titleStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
//合并样式
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Cell cell = row1.createCell(i);
cell.setCellStyle(titleStyle);
}
row1.getCell(0).setCellValue("用户测试数据");
// 处理标题
String[] titles = new String[]{"编号","姓名","手机号","入职日期","现住址"};
// 创建标题行
Row titleRow = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell = null;
for (int i = 0; i < titles.length; i++) {
cell = titleRow.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(titles[i]);
cell.setCellStyle(titleStyle);
}
// 处理内容
List<User> userList = this.findAll();
int rowIndex = 2;
Row row = null;
for (User user : userList) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getId());
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getUserName());
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getPhone());
cell = row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(sd.format(user.getHireDate()));
cell = row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellStyle(contentStyle);
cell.setCellValue(user.getAddress());
rowIndex++;
}
// 导出的文件名称
String filename="员工数据.xlsx";
// 设置文件的打开方式和mime类型
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
response.setHeader( "Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String(filename.getBytes(),"ISO8859-1"));
response.setContentType("application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet");
workbook.write(outputStream);
}